The record television audiences who watched the opening of the new season of the BBC’s Sherlock on New Year’s Day 2014 were doing what a significant portion of the Irish cinema audience had done a hundred years before (Barraclough). Several Irish picture houses began 1914 by showing Georges Tréville’s 1912 Franco-British production of The Beryl Coronet, the third of his Sherlock Holmes films for Éclair. Like the other film series of 1913, the Holmes series generated substantial publicity based on its relationship to a written text. A notice for the run of the first of the series, The Speckled Band, at Dublin’s Phoenix Picture Palace in November 1913 stressed that the series had “been produced under the personal supervision of Sir A. Conan Doyle” (Phoenix Picture Palace). The attractions for cinema owners and audiences of the adaption of a popular literary source were obvious:
The adventures of Conan Doyle’s great creation, Sherlock Holmes, are always fascinating, and the stories were literally devoured by readers as they issued from the press, and so great was the interest they compelled that they were many times reread. Their appearance now in picture form is certain to prove an immense attraction (ibid).
The New Year’s bills at Provincial Cinematograph Theatres’ Picture House, Sackville/O’Connell Street, Dublin and Picture House, Royal Avenue, Belfast were topped by The Beryl Coronet.
Although the importance of serials indicates one of the continuities in Irish cinema at the beginning of 1914, changes were also apparent. In his Christmas column, the Irish Independent‘s literary critic Terence O’Hanlon focused on the growing ubiquity of cinema. Surveying developments in the cinema industry around the world, he concluded:
That cinematography is entering more and more into the everyday life of the community is an obvious fact. Already it is playing an important part in commerce and education, in addition to its merits as a public entertainer. […] Each successive year will see further developments in the science, and additions to the long list of uses to which it has already been adapted (O’Hanlon).
Although O’Hanlon stresses commerce, education and science here, the most obvious manifestation of the cinema for ordinary people in Ireland was the increasing appearance of picture house on the streetscape of cities and towns. The Lockout of workers in Dublin had meant that building work on new picture houses – including the extensive renovations to Provincial’s luxurious Picture House, Grafton Street and two new premises in Phibsboro, the Phibsboro Picture House and the Bohemian Picture Theatre – had halted in that city, but this was not the case in Belfast. In its 1 January issue, the Bioscope heralded the arrival of two new picture houses in Belfast at the turn of the year (“Two New Halls for Belfast”). Both the Clonard Picture House on the Falls Road and the Central Picture Theatre in Smithfield opened on 22 December in time for the increased business at Christmas.
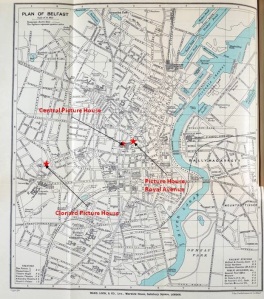
Map of Belfast in 1915 showing Clonard Picture House, Central Picture Theatre and Picture House, Royal Avenue.
Managed by W. J. Hogan, the Clonard had a facade executed in the Renaissance style and was praised for its ventilation and use of natural light. Its decorative features included a lobby finished in marble and terrazzo flooring and wood-panelled walls. Once patrons had been enticed inside, they could all enjoy an unobstructed view of the screen and an orchestra that included musician playing “piano, 1st and 2nd violins, bass, clarionet and trombone [who] co-operate in a delightful manner in accompanying the pictures” (ibid).
A less-elaborate conversion of a former jewellers, the Central ensured that it attracted as much of the attention of passersby as possible with an impressively lit facade:
The front is illuminated by hundreds of tiny coloured lamps and three powerful arcs the latter being hung from specially designed brackets, while on the roof is a large electric sign, with the words, “Picture Theatre” done in gold. The sign is of script pattern, and is so arranged as to be easily visible from the main thoroughfare of the city – Royal Avenue (ibid).
Both picture houses had their own generators, but also used mains electricity. The power at the Central was controlled from the projection box, where “two separate panels have been installed, change-over switches to the city’s supply being mounted in case of breakdown” (ibid). It was not the picture house generators but the mains supply that broke down on the evening of 2 January, when a six-minute blackout occurred while shows were in progress. Neither the Central, Clonard nor Royal Avenue appeared to have been affected,
the interruption being most keenly felt at seven of Belfast’s halls – the Alhambra, Panopticon, Silver, Mountpottinger Picturedrome, Kelvin, the Shaftesbury, and the Shankhill Picturedrome – and but for the timely intervention of the respective managers the alarm occasioned might have developed, in one of two cases, into panic (“Trade Topics”).
This surprising addition to the evening’s entertainment might have devised by one of the villains pursued by Sherlock Holmes.
References
Barraclough, Leo. “‘Sherlock’ Premieres to 9.2 Million Viewers in the U.K.” Variety 2 Jan. 2014. http://variety.com/2014/tv/news/sherlock-nabs-34-audience-share-for-bbc-in-u-k-1201021043/.
O’Hanlon, Terence. “Picture Houses: Big Boom in Bioscopes.” Irish Independent 23 Dec. 1913: 4.
“Phoenix Picture Palace.” Evening Telegraph 1 Nov. 1913: 6.
“Tenders Invited.” Irish Builder 2 Aug. 1913: 502.
“Trade Topics.” Bioscope.8 Jan. 1914: 95.
“Two New Halls for Belfast.” Bioscope 1 Jan. 1914: 31.

