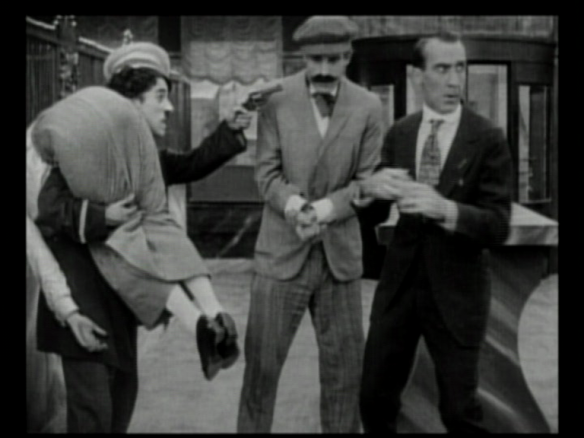
Framegrab from The Fight at St. Eloi (Britain: British Topical Committee for War Films, 1916); Imperial War Museums.
The London-based trade journal Bioscope opened its first June issue with an editorial entitled “The Moving Picture: The New National Weapon” and subtitled “A Force which Cannot Be Destroyed and Should Therefore Be Utilized.” “The new Defence of the Realm Regulations contain a warning that penalties will be incurred by the exhibition of unpatriotic cinematograph films,” it began, before confidently asserting:
We are happy to believe that the precaution was unnecessary. The power of the pictures has never yet been used in this country for the furtherance of disloyal or anti-British objects. It has, on the other hand, not seldom been employed with the utmost success in patriotic causes.
Nevertheless, the British government did see a reason for tighter legislative control of cinema in pursuit of the ideological goal of promoting patriotism, unanimity and support for recruitment in the context of a lengthy and costly war. The economic need to fund the war through increased tax had most directly affected cinema through the recently introduced Entertainment Tax.
In many ways, cinema in Ireland in June 1916 looked like a mature industry, regulated by these laws, but also highly cognizant of and largely aligned with the London-based trade. Even Ireland’s laggardly film production showed considerable development when the Film Company of Ireland press-showed its first production, O’Neil of the Glen, on 29 June at Dublin’s Carlton Cinema (“Irish Film Production”). The Bioscope was one of the ways in which this alignment was achieved, and although it was certainly read in Ireland, members of the Irish cinema trade might have been less confident of the claims of this editorial. In the same 1 June issue, the journal’s “Trade Topics” column published the assertion of J. Magner of the Clonmel Theatre that the Bioscope was the best of the cinema trade papers. And in 22 June issue, Irish columnist “Paddy” informed readers that the Bioscope was available at Mrs Dunne’s shop in Dublin’s Brunswick Street – close to the Queen’s Theatre, Norman Whitten’s General Film Supply, distributor Weisker Brothers, and other cinema businesses.
In the aftermath of the Easter Rising, however, it was questionable to what the Irish population at large was loyal. Support for the war still dominated the mainstream Irish press, but antiwar and pro-republican sentiments were becoming less marginal. By June, some theatres and picture houses anxious to maintain displays of their loyalty to the Crown – and by extension, that of their patrons – encountered protests. The large Theatre Royal had been one of the first places of amusement to open after the Rising, when it had offered British Army propaganda films. This did not, however, mean that its audience could all be considered loyalists.
On 26 June, for instance, William Charles Joseph Andrew Downes, a church decorator living at 15 Goldsmith Street, Dublin, was arrested for riotous behaviour during a live show at the Theatre Royal. He had shouted abuse related to the Boer War at a uniformed soldier who had responded to a magician’s call for a volunteer from the audience (“Scene in City Theatre”). The Boer War of 1899-1902 had been extremely divisive in Ireland, with popular support for the Boers’ stand against the British Empire extending from fiery speeches by Parnell’s Irish Parliamentary Party in Westminster to attacks on British soldiers in the streets of Dublin, and it was directly linked to the Rising in the person of executed leader and former Boer Irish Brigade major John McBride (Condon). As Downes was being escorted out the door of the Theatre Royal, he drew attention to the Irish republican badge he was wearing – a display of solidarity with the Easter rebels – and suggested that it was the reason he was being expelled.
Downes’ outburst could not be completely dismissed as the actions of a drunk – the arresting constable described him as neither drunk nor sober but “half-and-half” – and it was not isolated. The previous week, seven young people between the ages of 17 and 29 – four men and three women – had been charged in Dublin’s Police Court with offenses under the Defence of the Realm Act and with assaulting the constables who had attempted to seize the green flag at the head of a procession of 400 republican supporters that had been followed through the city centre by a crowd of around 2,000 (“Amazing City Scenes”). The crowd had also shouted republican slogans and booed and groaned passing soldiers. The mass arrests and deportations in May had failed to quell advanced nationalist activism that was now consciously identifying itself as republican.
This republican riot on Dublin’s streets provided an immediate if unacknowledged context for press commentary on the educational value of the official war films. “The boys of the future will have many advantages over the boys of the past,” observed the Dublin Evening Mail’s “Town Topics” columnist. “They will learn by picture-houses as well as by paradigms. It has been said that there is no Royal road to learning. There may be a Theatre Royal road, however” (“Town Topics”).
In a telling slippage, he was in fact discussing a new programme of official war films at the Gaiety Theatre rather than at the Royal. Although his point was about the ease or gaiety with which cinema could teach history, it is clear that this history would inculcate loyalty to the crown and war effort. “When I was in statu pupillari,” he continued,
history was taught me not without tears. The boys of the future will learn of the great war at the picture-palaces. I saw some of the official war films last week at the Gaiety Theatre. I saw the Irish regiments marching to Mass. I saw the heavy artillery attacking a German block-house. […] I saw our men in the trenches, preparing to seize the crater of a mine explosion. I saw them lobbing bombs like cricket balls at the enemy. Then I saw them – gallant Canadians at St. Eloi – fix bayonets and out over the parapet to charge across No Man’s Land and leap at the foe. Who would read the dull chronicles of Caesar of Livy after that?

Framegrab from Destruction of a German Blockhouse by 9.2 Howitzer (Britain: British Topical Committee for War Films, 1916); Imperial War Museums.
In making this argument, the Town Topics writer was aligning himself with the Bioscope early 1916 description of the cinema as the “nation’s historian.” Although certainly exciting, these official films were not mere entertainment but a new kind of visual historiography. And this was not just a boon for schoolboys but also a new historical method that could help historians to overcome the wartime measures introduced by governments to control the flow of information. He argued that while “[a]t the beginning of the war it was thought the historians would be bankrupt, because the censorship hid deeds of our men in the mystery of the night,” in fact, “[t]he cinema will save the historian, and at least help him to pay ten shillings in the pound.”
Other press coverage of the Gaiety shows gives further details of how this new history was presented and received. The choice of a large “legitimate” theatre such as the Gaiety rather than in a picture house associated the films with a site of serious cultural production aimed at a discerning audience. On the other hand, the Gaiety adapted picture-house exhibition practices in showing the films at three shows a day beginning at 3pm. “[T]he Gaiety Theatre opens a practically new chapter in its career,” the Freeman’s Journal commented, “by the fact that the attraction is not the familiar drama, musical or otherwise, but the production of a series of official war pictures which are, beyond all doubt, of transcendent interest” (“Amusements”). “In imagination,” observed the Irish Times, “one may see Irish soldiers at work and play, the Connaught Rangers and Munster Fusiliers amongst them, and Captain Redmond is seen leading his company to the front lines” (“Public Amusements”). Similar to other entertainments at the theatre, “a most excellent musical accompaniment is supplied by the Gaiety orchestra” (“Amusements”). Although music might contribute to the ease with which these images could be perceived, the musical director would presumably have had to be careful to avoid evoking not tears of schoolboy struggle but those of poignant loss among audience members with relatives and friends in France.
More chapters of this history that could – a least theoretically – be assimilated without tears, were on the way. “At the General Headquarters of the British Army in France,” reported the Dublin Evening Mail on 22 June, “there was last night exhibited before a large gathering of distinguished officers and their guests the latest series of the official war films, which in due course will be presented to the public at home and to neutral Powers, amongst which the desire to learn what our troops are really doing is unquestionable very keen” (“Pictures Taken at the Front”). This first run before an expert military audience could not, however, guarantee how resistant audiences in Ireland or elsewhere might react.
The Irish Catholic Church seemed to also believe that the cinema could not easily be destroyed and should therefore be, if not utilized for its own purposes, at least shaped by its ideology. With the appointment in June 1916 by Dublin Corporation’s Public Health Committee of Walter Butler and Patrick Lennon as film censors, a milestone was reached in the church’s campaign to introduce local censorship that would reflect a distinctly Irish Catholic sensibility (Rockett 50). Films shown in Ireland already bore the certificate of the British Board of Film Censorship, which had been established by the film trade as a form of self-regulation to avoid government-imposed censorship. Even as Butler and Lennon were being appointed, the British industry was discussing renewed government determination to introduce official censorship. Among the cases cited that raised this issues in London was the banning of A Tale of the Rebellion, a film about the Easter Rising that showed an Irishman being hanged (“London Correspondence”). Even as they announced the introduction of censorship in Dublin, however, the Irish Vigilance Association (IVA) expressed impatience with the lack of urgency demonstrated by the Corporation in appointing censors (“Film Censors for Dublin”).
From the IVA’s perspective, censorship was increasingly urgent given cinema’s growing appeal for the middle class, epitomized by improvements to cinematic music in June 1916. Three Dublin picture houses led the musical field: the city-centre Pillar and Carlton and the suburban Bohemian. Reviewing the Pillar at the end of June, the Irish Times revealed that its “orchestra including such favourites as Mr. Joseph Schofield, Mr. Harris Rosenberg, Mr. H. O’Brien, Miss Annie Kane and Mr. S. Golding, continue[s] to delight large audiences” (“Pillar Picture House”). Just a few doors away from the Pillar on Sackville/O’Connell Street, the Carlton boasted in Erwin Goldwater an internationally renowned violinist as its orchestra leader and soloist.
The Bohemian, however, outdid both of these when it engaged Achille Simonetti. “Dubliners will keenly appreciate the enterprise of the management of the Bohemian Picture Theatre in permanently engaging the services of one of the most noted violinists of the day in the person of Signor Simonetti,” the Dublin Evening Mail argued. “Henceforth Signor Simonetti will act as leader of the Bohemian orchestra – which has won such a wide repute – and will give solos, as well as Mr. Clyde Twelvetrees, Ireland’s greatest ’celloist” (“Play’s the Thing”). Simonetti debuted alongside Twelvetrees at the Bohemian on Whit Monday, 12 June 1916, when the bill was topped by Infelice (Britain: Samuelson, 1915), based on a novel by Augusta Evans-Wilson and starring Peggy Hyland. And if this was not enough to draw a large audience, the Bohemian announced that it would revise its pricing back to pre-Entertainment Tax rates, adding the line “We Pay Your Tax” to future advertisements.
The Bohemian added violist George Hoyle two weeks later. “The management now consider that they have the most perfect arrangement of stringed instruments and performers for a picture theatre,” the Irish Times reported (“Platform and Stage”). In a rare article focused on “Picture House Music,” Dublin Evening Mail columnist H.R.W. agreed that the Bohemian’s orchestra was the best in the city and that Simonetti’s “distinguished abilities attract large numbers of people from the most distant parts of the city.”
Commenting favourably on the tendency for picture-house orchestras to add strings and avoid brass and woodwind, s/he observed that while “the theatre orchestra was allowed to degenerate into mere noisy accompaniments to conversations in the auditorium during the interval,” in the picture house, “conversation is subdued, the music is subdued, the lights are subdued. The whole effect is soothing to the nerves.” Referring to Twelvetree’s impressive rendering of Max Bruch’s arrangement of “Kol Nidre,” s/he speculated that “the exact atmosphere is created by the fact that the solos are played in half light. The attention paid by the audience shows that this new feature is appreciated to the fullest extent.” S/he concluded that “the picture houses are affording us an opportunity of hearing the very best music, and in the hands of such fine artists as I have mentioned we can hear anything from a string quartet to a symphony.”
Although the official war films were not shown at the Bohemian, music of this kind could certainly play a role in assimilating the new tearless history.
References
“Amazing City Scenes.” Dublin Evening Mail 19 Jun. 1916: 3.
“Amusements: The Gaiety Theatre.” Freeman’s Journal 13 Jun. 1916: 6.
“Bohemian Picture Theatre.” Irish Times 13 Jun. 1916: 2; 20 Jun. 1916: 7.
Condon, Denis. “Politics and the Cinematograph in Revolutionary Ireland: The Boer War and the Funeral of Thomas Ashe.” Field Day Review Issue 4 (2008); and “Receiving News from the Seat of War: Dublin Audiences Respond to Boer War Entertainments.” Early Popular Visual Culture Vol. 9, No. 2 (2011).
“Film Censors for Dublin.” Freeman’s Journal 22 Jun. 1916: 6.
H.R.W. “Picture House Music: Its Growth and Development.” Dublin Evening Mail 28 Jun. 1916: 5.
“Irish Film Production.” Irish Times 30 Jun. 1916: 6.
“London Correspondence.” Freeman’s Journal 16 Jun. 1916: 4.
“The Moving Picture: The New National Weapon.” Bioscope 1 Jun. 1916: 955.
“Pictures Taken at the Front: Splendid New Series: Operator Gets Bullet Through His Cap.” Dublin Evening Mail 22 Jun. 1916: 3.
“The Pillar Picture House.” Irish Times 27 Jun. 1916: 6.
“Platform and Stage.” Irish Times 24 Jun 1916: 10.
“The Play’s the Thing.” Dublin Evening Mail 10 Jun. 1916: 6.
“Public Amusements: The Gaiety Theatre.” Irish Times 13 Jun. 1916: 2.
Rockett, Kevin. Irish Film Censorship: A Cultural Journey from Silent Cinema to Internet Pornography. Dublin: Four Courts, 2004.
“Scene in City Theatre: ‘There Is a Brave Man.’” Dublin Evening Mail 26 Jun. 1916: 4.
“Town Topics: Being a Casual Causerie.” Dublin Evening Mail 19 Jun. 1916: 2.