William Quinn – “The McCormack of the West” – was among the vocalists that the Pavilion engaged to attract the wealthy residents of Kingstown. Douglas Fairbanks’ The Good Bad Man (US: Fine Arts, 1916) was of secondary importance. Dublin Evening Mail 6 Aug. 1917: 2.
At the Kingstown (now Dún Laoghaire) Horticultural Show on 1 August 1917, local landlord Lord Powerscourt won not only the Challenge Cup for roses but also the Kingstown Picture House’s Cup for sweet peas (“Kingstown Horticultural Show”). That an Irish picture house was sponsoring such an event is indicative of cinema’s increasing integration into everyday life, and particularly its penetration of the realms occupied by the genteel gardeners of south County Dublin. Extra urgency had been added to the Kingstown’s courting of this audience by the reopening on 7 July 1917 of the Kingstown Pavilion. The Picture House had had the entertainment pickings of this wealthy town to itself since the Pavilion burned down on 13 November 1915. It would face well-advertised competition from the stylishly rebuilt Pavilion – designed by Coliseum architect Bertie Crewe – which sought to attract the affluent Kingstownites with vocal accompaniments to its films. You can get there [from Dublin] by tram or train,” an unnamed reviewer of the new picture house observed, “and whatever way you travel you will find plenty to please the eye en route” (“Cinema by the Sea”).
In late summer of 1917, cinema usefulness, its embeddedness in Irish society was evident not just in the importance of propagandistic films featuring soldiers at the front but also in its instructive role in relation to food production and child rearing. Lord Powerscourt may have been happy with decorative roses and sweet pea, but the food shortages caused by the continuing war meant that people unused to agricultural work were being urged to assist in the harvests and to grow their own food. A Women’s Land Army was established in mid-1917 to provide an agricultural workforce. Among the ways in which this force was to be promoted and trained was through “an excellent cinema film […] showing the work of women on the land” (“The Women’s Land Army”). “In these days of war savings and general cheeseparing,” J. B. Holland, the writer of the “Motor News” column in Dublin’s Daily Express, reported at the end of July 1917, “it is something worthy of note to find a brand new word added to our vocabulary, and one that you can use too in polite society. Well that is the word – ‘Agronomist.’” This expansion to the writer’s vocabulary came from a film exhibited “in a cubby-hole cinema in a Sussex village” and depicting “a number of Agronomists in the very act of agronomising (or whatever the verb may be) with the result that all of us, individually and collectively decided at once to ‘go thou and do like likewise’” (Holland).

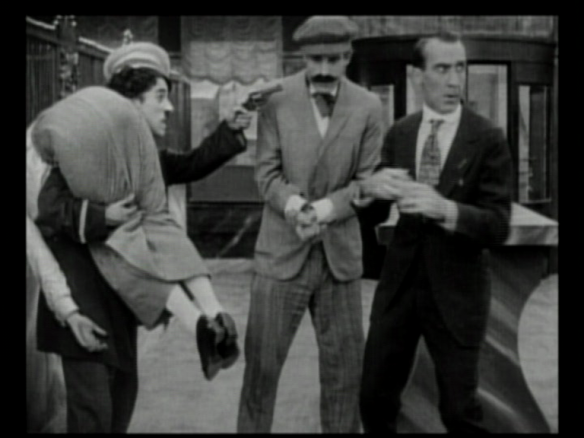
“You ought to know better than to send in seed potatoes for eating”; framegrab from Everybody’s Business (Britain: London, 1917), viewable here.
Holland did not name this film, but the Kingstown Pavilion had featured Everybody’s Business on its opening programme which may not have been an agronomizing film but was a fictional “food economy film.” It was, according to the trade journal Bioscope “in many respects the most important, and quite the most successful propaganda film that has been issued since the beginning of the war” (“Food Economy Film”). Although the “speeches of politicians, the canvassing by constituted societies, striking posters and press campaigns all have their effect,” the Bioscope argued that
a film which incorporates the essential parts of all these methods, contained in a pleasing and simple story, well told and admirably presented, must have a stupendous effect when circulated by a medium which has grown to be the most widely popular form of entertainment.

The Health Visitor (Dorothea Baird) teaches a new mother how to wash her baby in Motherhood (Britain: Trans-Atlantic, 1917). Image from the Women’s Film Pioneers Project.
Fiction films with such an explicit instructional intent were becoming more common. Just a few days before Pavilion audiences were warned off food wastage, audiences in other Irish cinemas were learning about child rearing from Motherhood (Britain: Trans-Atlantic, 1917). Sponsored by the National Baby Week Council, the film had been written by and featured Dorothea Baird, well-known stage and screen actress and wife of actor H. B. Irving. It was released for Britain and Ireland’s first National Baby Week that ran 1-7 July 1917. Alongside Dublin’s official events centred around an exhibition at the Mansion House, the Carlton Cinema showed Motherhood, which “illustrates how the rearing of children can be made a joyful thing and happy in its results, even in the poorest homes if only kindly interest and help is given to the mothers” (“‘Motherhood’ at the Carlton”). As well as a fictional narrative that demonstrated how a new mother (Lettie Paxton) is introduced to a School for Mothers by a Health Visitor (Baird), the film carried the endorsement of celebrities such as Baird and members of the social and political elite. “Mrs. Lloyd George, the Duchess of Marlborough, Lady Rhondda, Sir Richard Burbidge, Mrs. H. B. Irving, and many other notabilities connected with the National Baby Week Council have been specially filmed,” a Dublin Daily Express article observed, “so that their portraits may accompany the messages which they send to the nation through this epoch-making picture.” Lady Wimborne, wife of Ireland’s Lord Lieutenant, also endorsed the film, albeit belatedly, by attending a screening on 17 July 1917 at the Grafton Street Picture House (“To-Day in Brief”).
In the context of this increasing elite support for cinema, Winston Churchill was going somewhat against the grain when he decided following his appointment as Minister for Munitions not to fulfil his contract with the Ideal Film Renting to write the script for a film about the origins of the war (“Mr. Churchill Not to Write Film Stories”). But then, cinema had not been completely shaped to serve the war economy. It still represented a largely proletarian entertainment form and a space removed from work or fully rationalized leisure. It continued to arouse various kinds of anxieties in those in authority. The fear that picture houses provided sanctuary for shirkers and deserters was well illustrated by a parliamentary question in late July. Henry Dalziel asked Undersecretary of State for War Ian MacPherson what the British government was doing about English men who fled to Ireland to escape conscription. “Is he aware that there are hundreds of these men to be seen at cinemas in Dublin every night,” Dalziel asked MacPherson, addressing him in the third person, “and cannot he net more than a few back?” (“Hundreds at Dublin Cinemas”).

Still from the Clontarf Aquatic Festival, one of the items in Irish Events 3. Irish Limelight I:8 (Aug. 1917): 18.
Apart from the instructive fiction films, draft dodgers and other members of the cinema audience in Ireland were offered instructive local topical films, while the Film Company of Ireland was facing challenges finishing its epic Knocknagow. An increasing number of picture houses subscribed to the recently launched Irish Events newsreel, which had produced seven weekly issues and some specials by the end of August 1917. “The success of the Irish Topical Gazette has exceeded Mr. Whitten’s wildest anticipations,” observed Irish columnist Paddy in the Bioscope. “Many exhibitors have booked a contract for an extended period” (Paddy, 16 Aug.). And it was not just Irish exhibitors who could look forward to booking Irish Events because “Mr Whitten is making all arrangements for its showing in London” (Paddy, 23 Aug.).

A newsreel of Eamon De Valera’s victory in the Clare Election on 11 July 1917 could be seen on the screen at Dublin’s Rotunda on 16 July. Dublin Evening Mail 16 July 1917: 2.
Irish Events 2, the second weekly instalment of this newsreel, was issued on 23 July 1917 and featured five one-minute items that represented a mix of social and political events. As such, it resembled other newsreels, but Whitten appears to have conceived of it as primarily for social events because four of the items were of this type: The Mullingar Races, Trotting in Shelbourrne Park, A Garden Fete at Bushey Park and The Metropolitan Regatta at Island Bridge. The sole political item was De Valera after the East Clare Election (“Irish Topical Films”). The election film depicted an important event, but when viewed in the week of 23-28 July, it was not particularly timely as De Valera had won for Sinn Féin on 11 July. Indeed, a film of the election had been shown at the Rotunda – and undoubtedly other picture houses – beginning on 16 July, the same day as Irish Events 1 appeared but not as part of it.

An ad for Dublin’s Bohemian featuring a newsreel special on the Irish Convention; Dublin Evening Mail 26 Jul. 1917: 2.
With the emergence of Sinn Féin, political events in Ireland were moving fast, too fast for a weekly newsreel to keep up. It appears that Whitten planned to release the regular issues of Irish Events with items that could be planned in advance of its Monday release but also to release special “stop-press” films of events that could not be included in this way. This was the case when the Irish Convention, a meeting of Irish representatives convened to tackle the “Irish problem,” opened on Wednesday, 25 July. Whitten released a newsreel special of the Convention that was screened in Dublin’s Bohemian on 26 July. “Mr. Whitten is determined,” Paddy reported, “to let nothing stand in his way as regards securing the latest topical events” (16 Aug.).

Irish Events faced competition from the filmmaking activities of the Princess picture house in Rathmines; Dublin Evening Mail 19 Jul. 1917: 2.
By releasing the films of important political events quickly, Whitten maintained the scoop on his competitors. He faced competition on the filming of newsworthy events particularly from Gaumont, which had a substantial presence in Ireland and whose Gaumont Graphic newsreel was very popular. As well as this, Irish Events also faced local competition in its depiction of social events. Throughout July and August 1917, the Princess Cinema in Rathmines filmed such social events as the British Red Cross Garden Fete and the Opening of the Irish Counties’ Hospital by Lady Wimborne and even The Bushey Park Fete, which Whitten had also featured in Irish Events 2. While the Princess advertised that their films were exclusive – taken by them and not to be seen elsewhere – Irish Events was designed to be widely distributed. Whitten and his cameraman J. Gordon Lewis would have a busy autumn as they worked on Irish Events, on advertising films for Court Laundry and Paterson’s matches, and on an animated film with cartoonist Frank Leah.

Joseph Holloway’s sketch of Frank Fay as Beresford Pender in a stage adaptation of Charles J. Kickham’s Knocknagow at the Queen’s Theatre in July 1917. National Library of Ireland.
Although it had some organizational problems, Ireland’s other major indigenous film production company, the Film Company of Ireland (FCOI) also entered the somewhat crowded field of local factual filmmaking. Paddy reported that FCOI “have just finished an enormous scenic film dealing with the beauties of rural Ireland, and also containing many character studies and views of historic places” (23 Aug.). Rather than one long film, this was a series consisted of 20 one-reel films. These may have been among the company’s films that Paddy reported that Glasgow’s Square Film Company had arranged to distribute. FCOI managing director James Sullivan also told Paddy that their “almost completed” Knocknagow would be nine reels long, “the longest production ever made in the United Kingdom.”
Sullivan was eager to keep the much-anticipated adaptation of Knocknagow in the forefront of the media discussion of the company rather than its recent winding up proceedings. On 25 June 1917, his wife Ellen Sullivan, as a company creditor, had applied for its winding up in order that it could be restructured. During the proceedings, it emerged that she had given the company £500 and that it was running at a loss of £1,526 (“Film Company of Ireland”). The restructuring was necessary because James Sullivan’s co-director Henry Fitzgibbon had gone to America to promote the company but had decided not to return to Ireland. The proceedings caused some anxiety in those who were peripherally involved in FCOI. “I recently saw that the Film Co. of Ireland has been before the Court for winding up prior to reconstruction,” playwright Martin J. McHugh wrote to Joseph Holloway. “This may, and I hope will, mean only a delay in the resumption of their work; but somehow it damps one’s confidence in Irish enterprise, which does not seem usually to be blessed with good management” (Holloway, 7 Jul. 1917). McHugh had written two scripts for FCOI, “one long since paid for and photographed, and the other yet to be produced – and I wonder what will become of them.”
While the future of Irish fiction filmmaking looked uncertain at the end of summer 1917, instructive images of various kinds filled the screens.
References
“Cinema by the Sea.” Irish Limelight 1:9 (Sep. 1917): 4.
“Film Company of Ireland.” Daily Express 26 Jun. 1917: 3.
“The Food Economy Film: “Everybody’s Business”: A Stirring Appeal to the People.” Bioscope 14 Jun. 1917: 1050.
Holland, J. B. “Motor Notes.” Daily Express 30 Jul. 1917: 3.
Holloway, Joseph. Holloway Diaries. National Library of Ireland.
“Hundreds at Dublin Cinemas Every Night: Commons Questions.” Evening Herald 24 Jul. 1917: 1.
“Irish Topical Films.” Evening Telegraph 21 Jul. 1917: 4.
“Kingstown Horticultural Show: Decrease in Exhibits.” Daily Express 2 Aug. 1917: 7.
“‘Motherhood’ at the Carlton.” Daily Express 2 Jul. 1917: 7.
“Mr. Churchill Not to Write Film Stories.” Daily Express 21 Jul. 1917: 6.
Paddy. “Irish Notes.” Bioscope 5 Jul. 1917: 83; 16 Aug. 1917: 766; 23 Aug. 1917: 881.
“Seen and Heard: Notes and Notions on Men and Matters.” Evening Herald 22 Aug. 1917: 2.
“To-Day in Brief.” Daily Express 18 Jul. 1917: 4.
“The Women’s Land Army” Daily Express 9 Jul. 1917: 4.