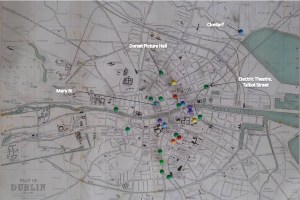
A little after 7pm on Friday, 6 February 1914, architect and inveterate theatregoer Joseph Holloway and his niece Eileen O’Malley arrived at Dublin’s Gaiety Theatre to find that the parterre was already full and there was standing room only in the upper circle. They decided not to stand for that evening’s final performance of the pantomime Jack and the Beanstalk, which was a benefit for comedian Jay Laurier, the actor who played Miffins. Instead they walked to the Nassau Street corner of Grafton Street to take a tram to the Dorset Picture Hall where they spent the evening watching a series of “interesting” but unnamed pictures (Holloway). It’s not clear why they passed the other picture houses along the tram route across the city to favour the Dorset, but Holloway seems to have taken a liking to the Dorset, having seen Kissing Cup (Britain: Hepworth, 1913) there with Eileen on 2 January and The Child from the Sea alone on 28 January. He had also recently seen Germinal (France: Pathé, 1913) at the Princess Cinema in Rathmines and the show of Kinemacolor films at the Queen’s Theatre.

Handbill for films at the Dorset during the week of 15-21 June 1914 with three changes of programme. National Library of Ireland.
Holloway’s diary entries on his visits to Dublin’s picture houses are both unique and frustrating, providing the only sustained first-hand account by an Irish cinemagoer of this period but also offering merely tantalizing details of his visits. This contrasts markedly with his often lengthy comments on the city’s theatrical shows, many of which he saw on their opening night. Although he was committed to the theatre, he had also become since 1910 – almost without realizing it himself, it seems – a regular picture-house patron. Although more detail on goings-on in cinemas from an audience member’s point of view would certainly be welcome, the way in which going to the picture house had become such a mundane activity is fascinating. In his diary, Holloway notes significant films alongside theatre shows at the start of a week and often integrates a film show into his schedule, sometimes choosing a film but often choosing to see whatever was on at a favoured picture house.
Holloway and other cinemagoers would have increasing choice as 1914 progressed. “Dublin has not by a long way stopped in its career of opening picture houses,” reveals Paddy in the trade journal Bioscope in early February 1914. He mentions plans to open 18 more cinemas in the city, with plans for eight already approved.
There is no doubt that some of these new fry will pay, because they are to be built in districts badly provided for in the matter of theatres, but when I hear that it is proposed to open three new houses in Grafton Street, and two more in Sackville Street, I wonder what will happen. (Paddy, 5 Feb).
Comments on the growing popularity of Dublin picture houses were not limited to the trade papers. “There can be no gainsaying the popularity of picture theatres in the Irish metropolis,” comments Irish Times columnist the Clubman. “They seem to be always crowded and their proprietors must be making plenty of money out of them. Of course, the ‘man in the street’ will tell you that ‘the pictures’ are only a ‘craze,’ but they are a craze which will, I think, live for some time in Dublin, at any rate (“Dublin Topics”).
It was not just in Dublin, and it would not be a passing craze. In mid-January 1914, the Bioscope’s “Jottings from Ulster” columnist noted that the
Belfast Corporation cinematograph inspector, Mr. Campbell, reported at the last meeting of the Police Committee, that on Christmas Day, Boxing Day, and the 27th ult., 124,087 persons patronised the fourteen picture theatres in the city. These figures show an increase of about 15,000 as compared with Christmas, 1912, It is of considerable interest to note that 124,000 is roughly one-third of the entire population of Belfast; it may, therefore, be taken that the cinema is growing in favour to an enormous extent. (“Jottings,” 15 Jan.)
These are very interesting figures, adding some statistical support to the impression conveyed by Holloway’s diary and newspaper and trade-press articles. It remains more difficult to discern a hundred years later the degree to which individual films that appear to do so actually address such important issues as women’s suffrage, the labour movement and Home Rule. These questions might without too much distortion be phrased in the language of 2014 as concerning the way in which new media engage with questions of the changing nature of work, gender inequality and national sovereignty.
Women’s suffrage was one of the most prominent political questions of the 1910s, kept in the headlines by suffragette activism, including that by the Irish Women’s Franchise League. Suffragettes in Ireland – but not Irish suffragettes – had most directly used the new cinema technologies as a form of protest on the evening of 18 July 1912, when as part of a wider protest, English suffragettes Mary Leigh, Gladys Evans and Lizzie Baker had attempted to set fire to Dublin’s Theatre Royal by igniting the highly combustible nitrate film in the theatre’s cinematograph box between evening shows. “Had the lighted matches come in contact with the films, the substances of which are, of course, highly inflammable, a terrible disaster might have to be chronicled” (“Serious Suffragette Outrage”). For this and for a hatchet attack on British prime minster HH Asquith’s carriage, in which Irish nationalist MP John Redmond was injured, Leigh, Evans and Baker were sentenced to prison terms in Mountjoy Jail, where they joined eight Irish suffragettes and began a hunger strike.
Belfast’s Panopticon advertises Asta Nielsen in The Suffragette (1913); Belfast Newsletter 3 Jan. 1914: 1.
Events such as these were fictionalized in the German film The Suffragette (Projektions AG, 1913), which offered Irish audiences the rare opportunity of seeing suffragettes on screen treated as something other than just comedy. Featuring the Danish star Asta Nielsen as Nelly Panburne – modelled on Christabel Pankhurst – the film shows how Nelly protests by breaking shop windows; is force-fed when she goes on hunger strike in prison; and carries a bomb intended to kill Lord Ascue, a British minister modelled on Asquith opposed to women’s rights. The film attempts to contain its radical energies with a romantic subplot that sees Nelly save Ascue from the bomb and marry him. Despite the closeness of the film to actual events, the Belfast Newsletter commented that when it was exhibited in January 1914 at the Panopticon Picture Theatre, it “creates great merriment. Asta Neilson, described as the greatest of all picture artists, is seen at her best” (“Panopticon”).

- The confrontation between Irish unionists and nationalists had become such a part of popular discourse in Britain in early 1914 that this ad for films that had nothing to do with Ireland could expect to draw attention by using the names of Edward Carson and John Redmond as if they were prize fighters. Bioscope 12 Mar. 1914, p. 1186.
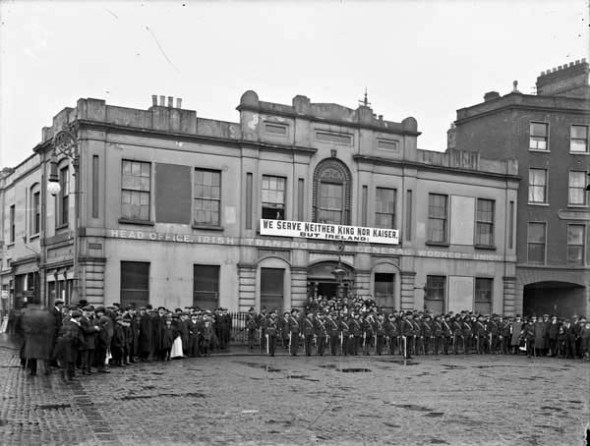
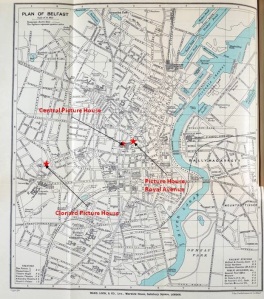
Perhaps the importance of the political events of a different kind in Belfast was among the factors that inclined the Newsletter towards downplaying a fictional representation of the suffrage movement. To keep up pressure on Asquith’s government, Edward Carson again visited Belfast In mid-January 1914 to rally unionist opponents of Irish home rule and review the massed ranks of the Ulster Volunteer Force prepared violently to resist the imposition of home rule. Such nationalist newspapers as Dublin’s Evening Telegraph and Belfast’s Irish News presented unionist demonstrations as a farce and drew attention instead to the counter-demonstration in Belfast led by nationalist MP Joseph Devlin (“Carson Comedy Co.,” “U.V.F. Comedy,” “Mr. Devlin, M.P., in West Belfast”). The unionists, however, again proved themselves more competent with the new cinematic medium. A newsreel camera was again in Belfast to record and relay images not of Devlin but of Carson, and this time, it was operated by Dublin-based Norman Whitten, who filmed the demonstration for Weisker Brothers, a firm to which he had recently affiliated (Paddy, 29 Jan.). Paddy commended Whitten for having the film of Carson ready to screen at Belfast’s Picture House, Royal Avenue on the evening of the rally (ibid).
Of more immediate concern to Dublin’s media from mid-January to early February was the end of the Lockout with the defeat of the striking workers. For the first three days of the week beginning Monday 19 January, the Evening Telegraph’s notice for the Phoenix Picture Palace recommended A Leader of Men, “dealing in a thrilling and sensation manner with an organised strike in a big shipbuilding industry. It is decidedly a picture that will appeal strongly to all at the present time” (“Phoenix Picture Palace”). On the same day, the Telegraph was reporting the “Collapse of Strike: No Food and No Money: Mr. Larkin Advise Men: To Go Back to Work: But to Sign No Agreement” (“Collapse of Strike”). If that drama was too close for comfort to current events, audiences could also enjoy more diverting material on the same bill in the dramas Fortune’s Turn and The Dumb Messenger and the comedies The Honeymooners, When Love Is Young and Cartoons, Mr Piffle. As well as this, to whom and in what way the film would appeal is not clear given that it is unlikely many of the workers impoverished by months of strike could have afforded to attend.
Nevertheless, as cinema continued to develop and picture houses occupied more spaces on the Irish streetscape, films would attract audiences not only by providing escape but also by confronting – both directly and obliquely – important political issues.
References
“Carson Comedy Co.: Performing in Belfast To-Day.” Evening Telegraph 17 Jan. 1914: 6.
“Collapse of Strike.” Evening Telegraph 20 Jan. 1914: 3.
“Dublin Topics by the Clubman.” Irish Times 31 Jan. 1914: 4.
Holloway, Joseph. Holloway Diaries. National Library of Ireland. 6 Feb. 1914: 295.
“Jottings from Ulster.” Bioscope 15 Jan. 1914: 263.
“Mr. Devlin, M.P., in West Belfast: Great Rallies of the Progressive Forces Hear Inspiriting Addresses.” Irish News 19 Jan. 1914: 5-6.
“Phoenix Picture Palace.” Evening Telegraph 20 Jan. 1913: 2.
Paddy. “Pictures in Ireland.” Bioscope 29 Jan. 1914: 454.
Paddy. “Pictures in Ireland.” Bioscope 5 Feb. 1914: 547.
“The Panopticon.” Belfast Telegraph 6 Jan. 1914: 9.
“Serious Suffragette Outrage: Two Attempts to Set Fire: To the Theatre Royal: An Explosive Used: A Panic Avoided.” Freeman’s Journal 19 Jul. 1912: 6.
“U.V.F. Comedy: Parade of the East Belfast Regiment: Inspection by Sir E. Carson.” Irish News 19 Jan. 1914: 7.